Introduction to CABG in Singapore
Narrowing of blood vessels on the heart or coronary arteries is typically caused by atherosclerosis. This can result in ischaemic heart disease (IHD) or coronary artery disease (CAD). Contributory factors include diabetes mellitus, high blood pressure, high blood cholesterol, heavy smoking, family history and possibly high stress lifestyle and diet.
Chest pain or angina is the primary symptom of coronary artery disease (CAD). It is typically a squeezing chest pain that may spread to the neck, jaw, shoulder or abdomen. The pain is a signal from the heart that it is receiving insufficient blood and oxygen. However sometimes chest pain can be silent especially in patients with long standing diabetes or kidney failure. Other symptoms may include:
- Shortness of breath
- Irregular heartbeats (palpitations)
- Dizziness
- Nausea
- Sweating
Treatment may be lifestyle changes, medications, a procedure called percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) or surgery called coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG).
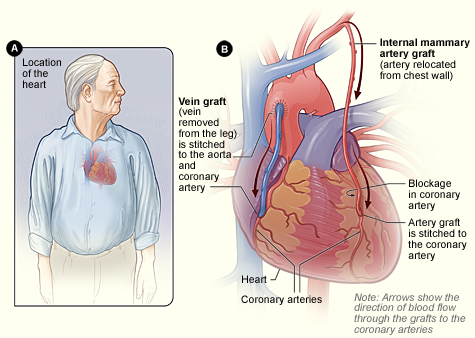
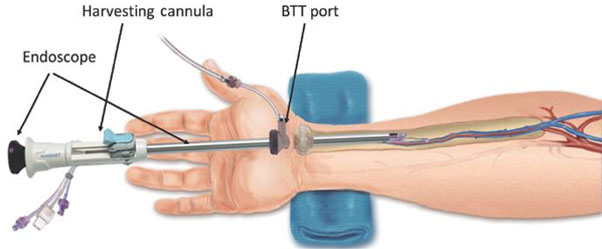
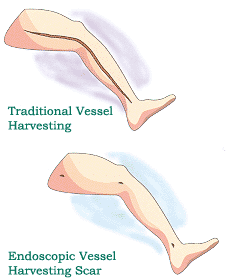
CABG is a surgery which specifically targets Coronary Heart Disease. It improves blood flow to the heart and relieves fatigue, chest pains and promotes better health for your circulatory system.
Seasoned practitioner Dr Loh Yee Jim conducts CABG in Singapore. With numerous years of experience as a surgeon in Singapore, Dr Loh has performed many CABG treatments to help patients in Singapore.
More about Dr Loh
Besides CABG, Dr Loh is an active researcher and contributor in the medical field. Using his experience as a practitioner, he contributes actively to research on CABG and medicine in Singapore.
Currently, Dr Loh is also a member of the Residency Advisory Committee (RAC). He continues to use his skills and expertise to spearhead research and initiatives to improve overall health in the nation.
How to contact us
If you have any questions about Dr Loh or CABG, feel free to reach out to us by clicking here.